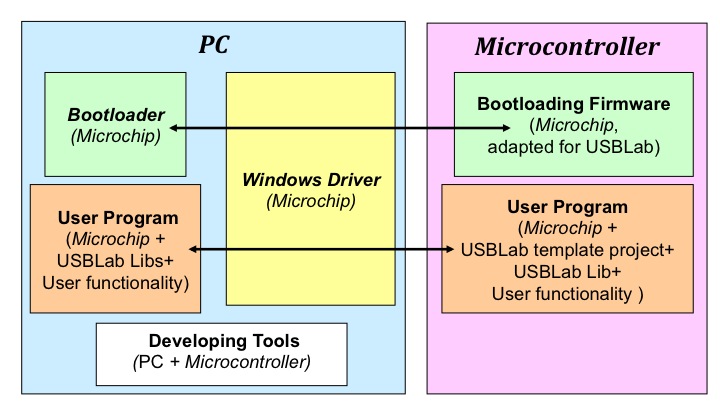
The pieces of software insalled in the PC can be organized in 4 big groups : the bootloader to install the microcontroller program, the libraries used to develop the USBLab user program in the PC, and the developing tools used to develop the software both for the PC and the microcontrollers, and the USB Windows driver to communicate the PC with the PIC18F4550. The relationships among these pieces of sofware and with the pieces of software and the microcontroller are schematized in the following figure. The software of each of the groups is shortly described next.
Bootloader
Microchip provides with its development tools a bootloader to download the programs in the microcontrollers directly using the USB port. To be able to use it, a bootloading firmware (adapted for the USBLab from the code provided by Microchip to develop it) to has to be downloaded first in the microcontroller using a normal programmer and an USB driver (see below) installed in the PC.
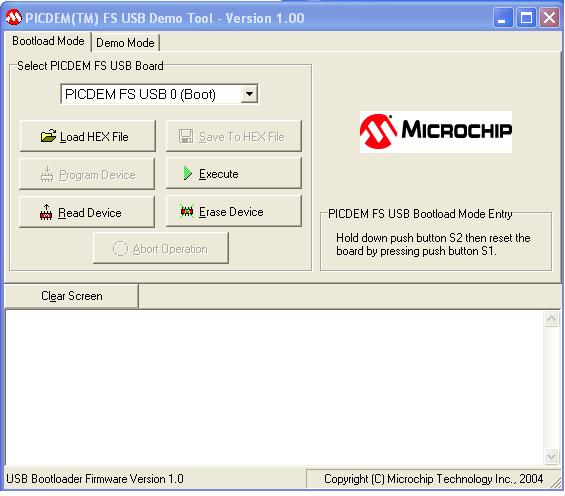
Its main window is represented in the following figure. From it, the microcontroller connected to the PC through the USB port where the software has to be installed is selected, as well as the hex code to download in the microcontroller.
PC libraries for the PC user program
In order to facilitate the programming of the PC that monitors/controls a system through using a USBLab connected with it, we have developed several libraries in different programming languages such as C, Matlab and Simulink. In the following sections, we shortly introduce their characteristics, organized according to its language.
C Libraries
Currently, the USBLabs can be monitorized/controlled from a PC via the USB port, radio or bluetooth. The radio communication requires a USBLab programmed as a radio server that is connected to the PC through the USB. Therefore, there are only two ways of directly communicating the PC with the USBLab plugs into it : through the USB and through the bluetooth. In order to support the communication of the PC with the USBLab via the USB and bluetooth port we have developed two different libraries in C:
The first is the USBBase Library, which is in charge of supporting the communication via the USB port. To develop it, we use the functionality provided by Microchip to communicate with its USB microcontrollers.
The second is the USBUART Library, which is in charge of supporting the communication via the serial port or bluetooth (mounted by the PC as a serial communication port).
Matlab toolbox
The Matlab toolbox has been developed to let users to communicate with the USBLab programmed for different types of communication, directly from Matlab. The different types of communications are supported by our two C libraries (see section above). The functions of the toolbox can be grouped in 3 subsets : the first to control the USBLabs directly connected to the PC USB port, the second to control the remote USBLabs programmed as a USBLab radio client through the USBLab radio server connected to the PC USB port, and the third to control directly the remote USBLabs programmed as a serial port/bluetooth client. The functions within each group are differentiated by its starting name (pic, wpic, bpic) and the functionality is replicated, with its corresponding particularities, through the different groups.
The Matlab toolbox is also used to develop and debugg new programs from the USBLab microcontroller. In order to do that, the use Matlab to read and write directly the registers of the microcontroller, using in Matlab a similar order than the one they will use in the micro. After the program is debugged and working, it can be written following the microcontroller usual instuctions and downloaded in the micro.
Simulink toolbox
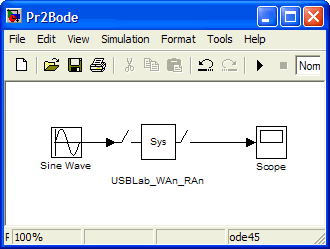
In order to be able to control the USBLab from Simulink, we have also developed the Simulink models for a few applications of the USBLab. With them, and with an USBLab plugged into the USB port of the PC, we can control systems with input/output analog signals. Following the same strategy, other models can be developed too, for systems controlled with other signals and/or USBLab programmed differently, using the USBLab C library functions. As an example of use, the following figure shows a Simulink model that includes a USBLab model for input/output analog signals to obtain the Bode diagram of a system.
Developing tools
The third group of software consists on the developing tools used to develop the user programs for the PC and for the PIC18F4550 in the microcontroller.
Developing tools for the PC user programs
The tools that are used for developing the user software in the PC are either a C compiler, Matlab or Simulink. As the C compiler we have used the Visual C++ 6.0 or the Borland Builder C++ 6.0.
Developing tools for the mircocontroller user programs
The microcontroller user programs are the MPLab IDE and the MPLab C compiler for the PIC18 family. Both can be donwloaded from the Microchip web page.
Windows USB Driver
Finally, in order to communicate with the microcontroller of the USBLab via the USB port, either to re-program it or to monitorize/control the USBLabs programmed to be plugged in the USB port, Microchip provides a driver for Windows that has to be installed in the PC.